Project: Research Intern
Location: Future Transport Power Lab, KAIST, Korea
(May 2022 - Aug 2022)
Analysis of Battery Efficiency, Heat Capacity and CO2 Emission for Electric Scooters
Abstract
This report consists mainly of the efficiencies in electric scooters and emission rates of CO2. In contrast to the belief that uses of electric scooters are eco-friendly throughout the world, CO2 emission rates from the production of electricity are not considered. The report, therefore, includes CO2 emission rates, electrical fuel efficiencies, and efficiencies of discharging and charging based on the temperature of the battery. In this experiment, two different methods are used for data collection: a real driving test and a chassis dynamometer test. With each method of data collection, single charge / full charge driving tests were performed. In the experiment, the efficiencies of charging and discharging resulted in 95.2%. The average fuel efficiency is calculated to be 120.51 km/kWh when the outdoor temperature is above 30 ℃ and is calculated to be 108.26 km/kWh below 30℃. In addition, electric fuel efficiencies increased with the decrease in speed; 122.19 k m/kWh at 13.80 km/h, 105.57 km/kWh at 15.50 km/h, 96.80 km/kWh at 22.50 km/h. The emission rates of CO2 show to be 3.89 g/km above 30℃ and 4.32 g/km below 30℃.
Using the results obtained from the real driving test and the chassis dynamometer test, we concluded that electric fuel efficiencies increase with the increase in temperature, decreasing the emission rates of CO2. On the other hand, identifying the correlations between the temperature and efficiencies of charging and discharging was not practical. The result of the experiment was not accurate due to the source of errors. The main source of error is that the control and observation for data collection from the battery management system (BMS) are impractical, in which the state of charge (SOC) is not obtainable. In order to obtain accurate results, it is essential to collect information from BMS. This experiment is to understand the overall relationship between the battery and the temperature.
Link:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1V1Vrj0aywZWnbWnIn5IqoarHPA9MUQHqewRx0vzxyrQ/edit?usp=sharing
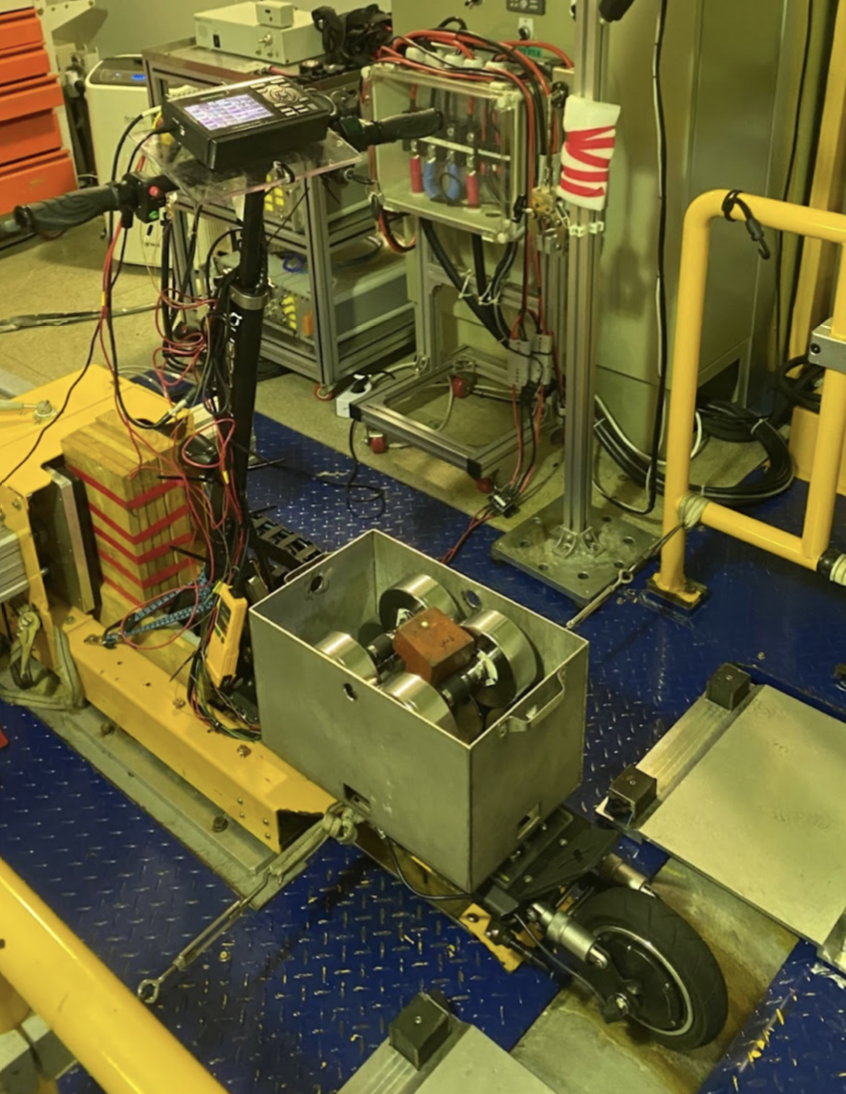
The chassis dynamometer test